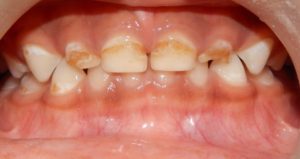
1.What is Early Childhood Caries(ECC)/ Baby Bottle tooth Decay & Severe Early Childhood Caries( S-ECC)?
ECC is the presence of one or more decayed, missing, or filled tooth surfaces in any primary tooth in a child under the age of six years. In children younger than three years of age, any sign of smooth surface caries is indicative of severe early childhood caries
It is a serious form of decay among young children is baby bottle tooth decay. This condition is caused by frequent and long exposures of an infant’s teeth to liquids that contain sugar. Among these liquids are milk (including breast milk), formula, fruit juice, sodas and other sweetened drinks.
Putting a baby to bed for a nap or at night with a bottle other than water can cause serious and rapid tooth decay. Sweet liquid pools around the child’s teeth giving plaque bacteria an opportunity to produce acids that attack tooth enamel. If you must give the baby a bottle as a comforter at bedtime, it should contain only water. If your child won’t fall asleep without the bottle and its usual beverage, gradually dilute the bottle’s contents with water over a period of two to three weeks.
After each feeding, wipe the baby’s gums and teeth with a damp washcloth or gauze pad to remove plaque. The easiest way to do this is to sit down, place the child’s head in your lap or lay the child on a dressing table or the floor. Whatever position you use, be sure you can see into the child’s mouth easily.
In younger children avoid exposure to food containing high amount of sugar like biscuits, cookies, jams, caramel which can add to the already damaged tooth
